Services
testing the potency of EVs
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) play an essential role in cellular communication by transporting proteins, lipids as well as nucleic acids. Several in vitro bioassays have been established to test the potency of extracellular vesicles such as assays to test for e.g. anti-inflammatory, neo-angiogenic, anti-fibrotic or wound healing activities.
General information
Potency assays: Evercyte has established cell-based assays to test anti-inflammatory , anti-fibrotic, neo-angiogenic activities of extracellular vesicles as well as fibroblast-growth promoting or senomorphic activities.
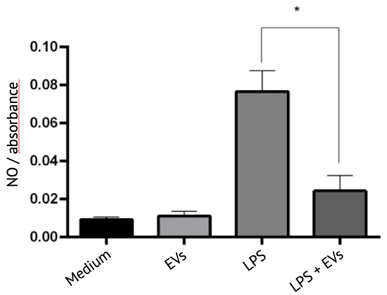
Testing anti-inflammatory activity of EVs
Testing anti-fibrotic activity of EVs
myofibroblast differentiation
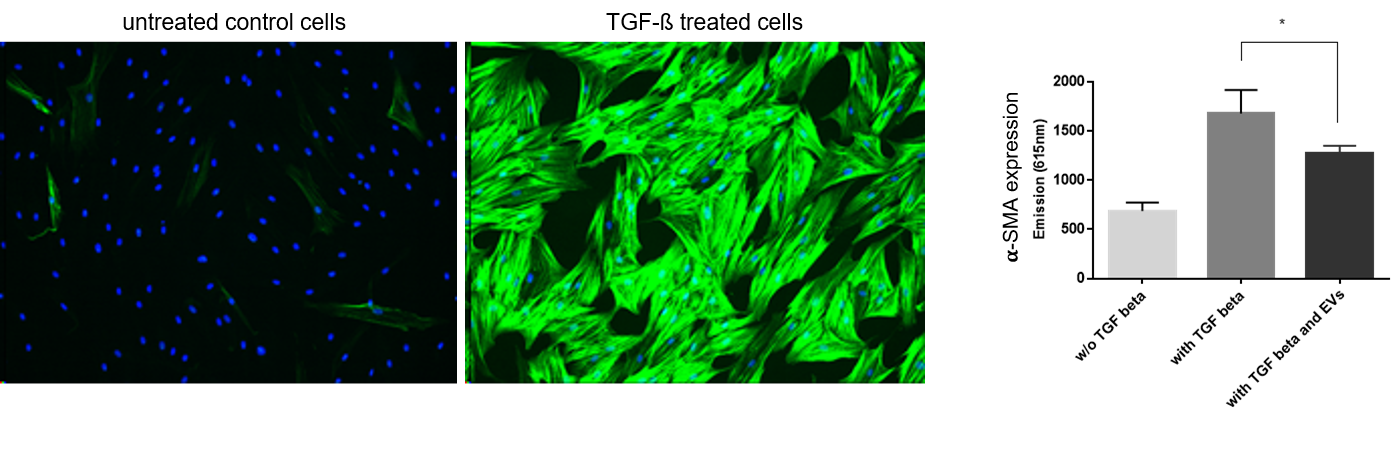
Treatment of human dermal fibroblasts (fHDF/TERT166) with transforming growth factor ß (TGF-ß) induces the expression of alpha smooth muscle actin (alpha-SMA / green fluorescence, cell nuclei are counterstained with DAPI), which is a key event in physiological and pathological tissue repair.
Extracellular vesicles from mesenchymal stem cells significantly reduce expression of alpha-SMA after TGF-ß treatment (right). These data indicate that EVs from these cells inhibit myofibroblast differentiation and might exert anti-fibrotic activity.
Testing neo-angiogenic potential of EVs
Sprout formation from endothelial spheroids
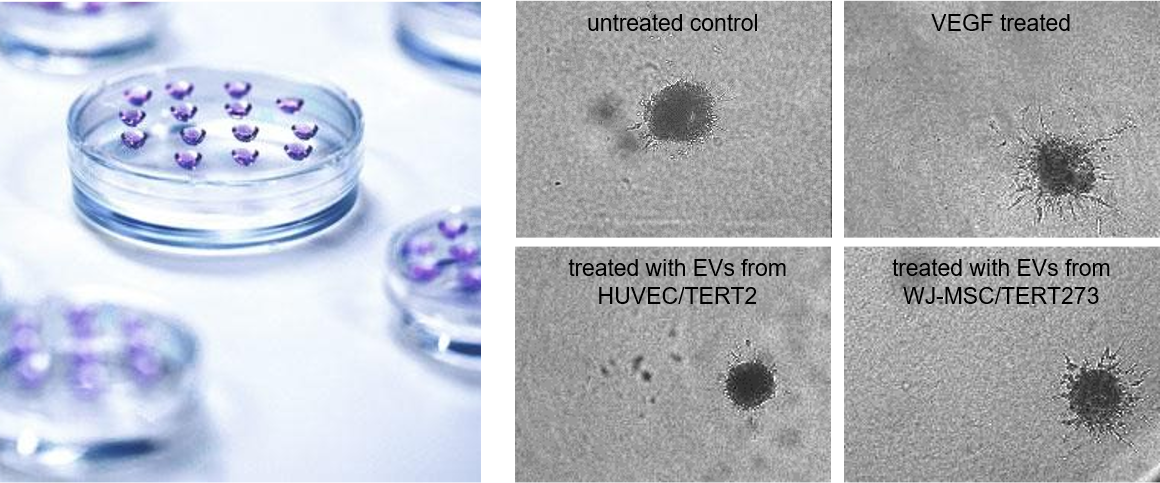
Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC/TERT2), grown as 3D spheroids in hanging drops (left picture) are embedded in a collagen matrix. Treatment of these spheroids with vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) induces the formation of sprouts. A similar effect is seen when spheroids are grown in the presence of extracellular vesicles from mesenchymal stem cells indicating neo-angiogenic potential of the EV preparation.
Testing wound healing activity of EVs
fibroblast growth promoting activity / scratch assay
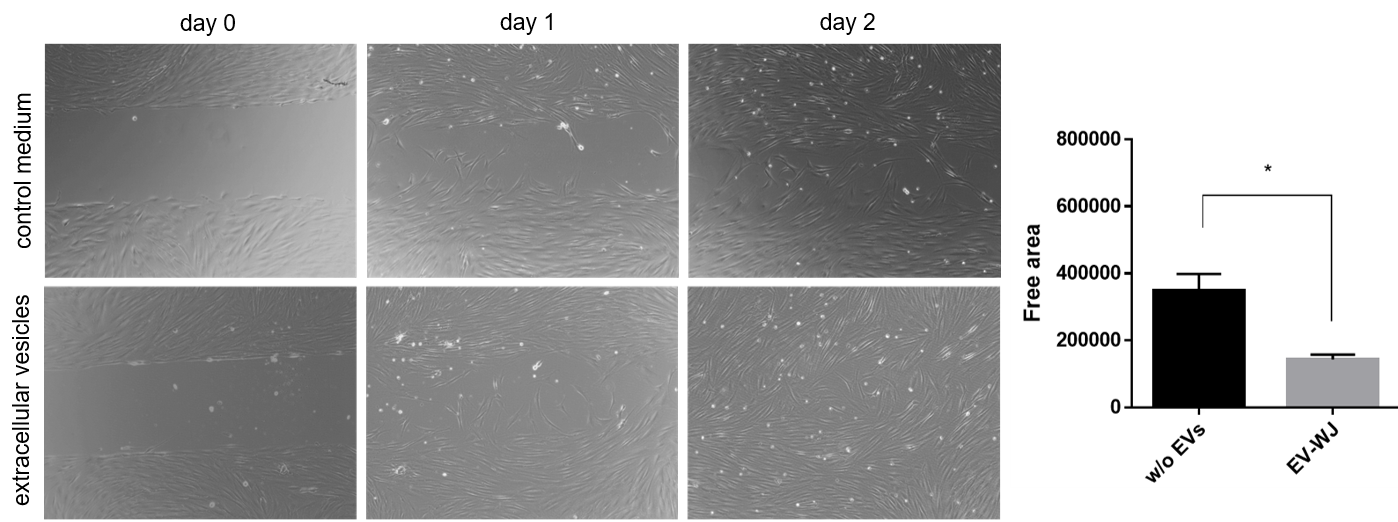

Telomerized human fibroblasts (fHDF/TERT166) are seeded into chamber slides and a physical gap within the monolayer is created followed by monitoring the process of cell migration into the gap. Significantly less free area between the cells is detected upon addition of extracellular vesicles from mesenchymal stem cells.
Customer Reviews
“I have had the pleasure of working with Evercyte for the last few years. We continually rely on Evercyte because of the high-quality data that they produce, their diligent responsiveness, and their excellent customer service.”
Josh Garlich, Senior Research Scientist, Apellis Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
"Cytonus has been working with Evercyte from many years as they are a trusted partner and have always delivered the highest quality cell lines to advance our platform. We routinely draw on their expertise to meet cellular engineering challenges and they have not disappointed."
Remo Moomiaie-Qajar, Cytonus Therapeutics, Inc.
Customer Reviews
“I have had the pleasure of working with Evercyte for the last few years. We continually rely on Evercyte because of the high-quality data that they produce, their diligent responsiveness, and their excellent customer service.”
Josh Garlich, Senior Research Scientist, Apellis Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
"Cytonus has been working with Evercyte from many years as they are a trusted partner and have always delivered the highest quality cell lines to advance our platform. We routinely draw on their expertise to meet cellular engineering challenges and they have not disappointed."
Remo Moomiaie-Qajar, Cytonus Therapeutics, Inc.