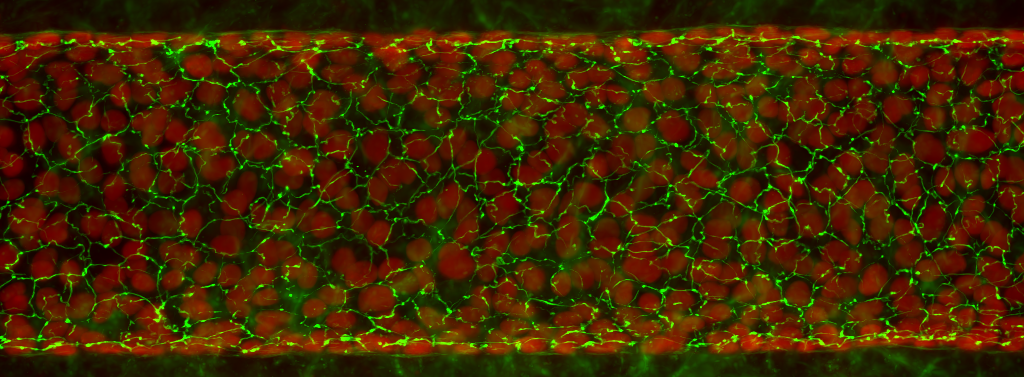
Kidney
RPTEC/TERT1
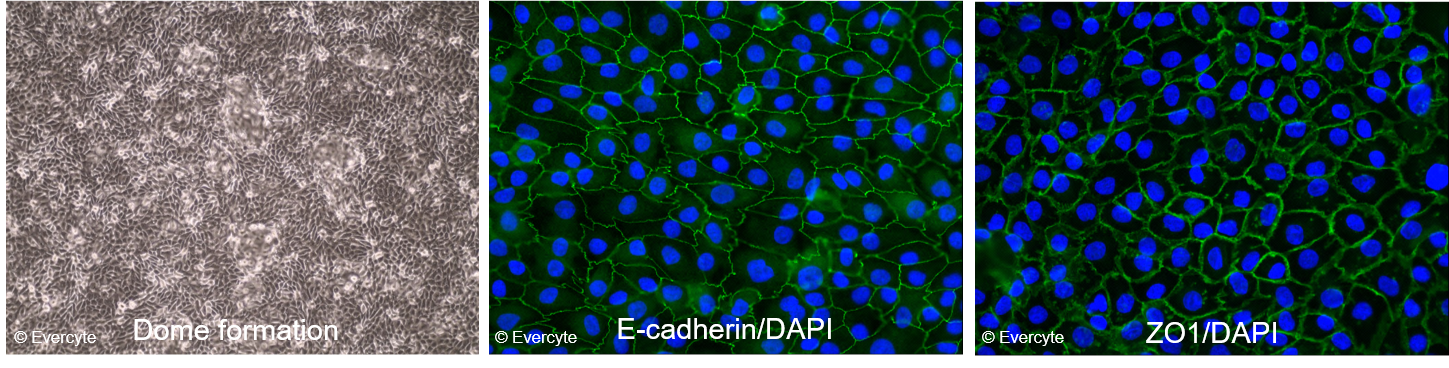
Evercyte’s human renal proximal tubular epithelial cell line RPTEC/TERT1 can be grown without limitations while maintaining expression of cell type specific markers and function. Therefore, these cells are useful to study kidney transport functions, kidney diseases or diabetes and to test new drugs for cytotoxic effects. Additionally, the cell line is the perfect starting material for genetic engineering to create important disease models.
General information
Cat#: CHT-003-0002
Morphology and marker expression
FAQs
In vitro propagation
ProxUp2 medium (Evercyte, Cat # MHT-003-2)
DMEM/Ham´s F12 (PAN Biotech, Cat# P04-41154)
10 mM HEPES-buffer (Sigma Aldrich, Cat# H0887)
0.5% FBS (PAN Biotech, Cat# P30-3031)
10 ng/ml hEGF (Sigma Aldrich, Cat# E9644)
5 pM 3,3′,5-Triiodo-L-thyronine sodium salt (Sigma Aldrich, Cat# T6397)
3.5 µg/ml L-Ascorbic Acid (Sigma Aldrich, Cat# A4544)
5 µg/ml Transferrin Holo (Merck Millipore, Cat# 616424)
25 ng/ml Prostaglandine E1 (Sigma Aldrich, Cat# P8908)
25 ng/ml Hydrocortisone (Sigma Aldrich, Cat# H0396)
8.65 ng/ml Sodium-Selenite (Sigma Aldrich, Cat# S5261)
100 µg/ml G418 (InvivoGen, Cat# ant-gn-5)
5 µg/ml Insulin (Sigma Aldrich, Cat# I9278)
Additional material & reagents
Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) (Sigma, Cat# D8537)
Trypsin inhibitor (Gibco, Cat# R007100)
0,05 % Trypsin-EDTA (Gibco, Cat#25300-054)
Passaging of cells
For detachment of the cells remove and discard the culture medium and wash the cells once with PBS (about 160 µl/cm²). Remove PBS completely.
Cryopreservation
Freezing medium
CryoStor® cell cryopreservation medium CS10 (Sigma Aldrich, Cat# C2874)
Additional material & reagents
Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) (Sigma, Cat# D8537)
0,05 % Trypsin-EDTA (Gibco, Cat# 25300-054)
Trypsin inhibitor (Gibco, Cat# R007100)
Freezing of cells
Detach the cells from the culture vessel by using Trypsin and Trypsin-Inhibitor (Protocol passaging of RPTEC/TERT1).
Thawing of cells
Original Evercyte cells are to be thawed in a T25 roux flask
Product data sheet – certificate of analysis
Protocols
Data on Markers and Functions
Selected publications
Carta G, van der Stel W, Scuric EWJ, Capinha L, Delp J, Bennekou SH, Forsby A, Walker P, Leist M, van de Water B, Jennings P. Transcriptional landscape of mitochondrial electron transport chain inhibition in renal cells. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2023 Dec;39(6):3031-3059. doi: 10.1007/s10565-023-09816-7.
Schreiber P, Friedrich AK, Gruber G, Nusshag C, Boegelein L, Essbauer S, Uhrig J, Zeier M, Krautkrämer E. Differences in the Susceptibility of Human Tubular Epithelial Cells for Infection with Orthohantaviruses. Viruses. 2023 Jul 31;15(8):1670. doi: 10.3390/v15081670.
Namazian Jam N, Gottlöber F, Hempel M, Dzekhtsiarova Y, Behrens S, Sonntag F, Sradnick J, Hugo C, Schmieder F. Microphysiological Conditions Do Not Affect MDR1-Mediated Transport of Rhodamine 123 above an Artificial Proximal Tubule. Biomedicines. 2023 Jul 20;11(7):2045. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11072045.
Pearson A, Haenni D, Bouitbir J, Hunt M, Payne BAI, Sachdeva A, Hung RKY, Post FA, Connolly J, Nlandu-Khodo S, Jankovic N, Bugarski M, Hall AM. Integration of High-Throughput Imaging and Multiparametric Metabolic Profiling Reveals a Mitochondrial Mechanism of Tenofovir Toxicity. Function (Oxf). 2022 Dec 24;4(1):zqac065. doi: 10.1093/function/zqac065.
Piossek F et al. Physiological Oxygen and Co-Culture with Human Fibroblasts Facilitate in Vivo-like Properties in Human Renal Proximal Tubular Epithelial Cells. Chemico-Biological Interactions, vol. 361, 2022 Jul. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2022.109959.
Merches K, Breunig L, Fender J et al. The potential of remdesivir to affect function, metabolism and proliferation of cardiac and kidney cells in vitro. Arch Toxicol 96, 2341–2360. 2022 May. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-022-03306-1
Glykofridis IE, et al. (2021) Loss of FLCN-FNIP1/2 induces a non-canonical interferon response in human renal tubular epithelial cells. eLife. 2021; 10: e61630 www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7899648/
Ranninger C., et al. (2015) Nephron Toxicity Profiling via Untargeted Metabolome Analysis Employing a High
Performance Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry-based Experimental and Computational Pipeline. J BiolChem. 2015 Jul 31;290(31):19121-32. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26055719/
Assessments. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2015 Jul;166(1):66-71. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25893367/
Maschmeyer I, et al. (2015) A four-organ-chip for inter-connected long-term co-culture of human intestine, liver, skin and kidney equivalents. Lab Chip. 2015 Jun 21;15(12):2688-99.https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25996126/
pathways for chemical testing. Toxicol In Vitro. 2015 Jan 13. pii: S0887-2333(14)00251-3. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25596134/
transcriptomic study. Toxicol In Vitro. 2015 Dec 25;30(1 Pt A):106-16. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25450743/
Wilmes A, et al. (2014) Evidence for a role of claudin 2 as a proximal tubular stress responsive paracellular water channel. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2014 Sep 1;279(2):163-72. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24907557/
Simon BR, et al. (2014) Cadmium alters the formation of benzo[a]pyrene DNA adducts in the RPTEC/TERT1 human renal proximal tubule epithelial cell line. Toxicol Rep. 2014 Jul 14;1:391-400. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25170436/
Fliedl L, Wieser M, Manhart G, Gerstl MP, Khan A, Grillari J, Grillari-Voglauer R. (2014) Controversial role of gammaglutamyl transferase activity in cisplatin nephrotoxicity. ALTEX. 2014;31(3):269-78. doi: Epub 2014 Mar 21. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24664430/
Aschauer L, et al. (2013) Delineation of the Key Aspects in the Regulation of Epithelial Monolayer Formation. Mol Cell Biol. 2013 Jul;33(13):2535-50. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23608536/
Radford R, Slattery C, Jennings P, Blacque O, Pfaller W, Gmuender H, Van Delft J, Ryan MP, McMorrow T. (2012) Carcinogens induce loss of the primary cilium in human renal proximal tubular epithelial cells independently of effects on the cell cycle. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2012 Apr 15;302(8):F905-16. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00427.2011. Epub 2012 Jan 18. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22262483/
Wilmes A, Limonciel A, Aschauer L, Moenks K, Bielow C, Leonard MO, Hamon J, Carpi D, Ruzek S, Handler A, Schmal O, Herrgen K, Bellwon P, Burek C, Truisi GL, Hewitt P, Di Consiglio E, Testai E, Blaauboer BJ, Guillou C, Huber CG, Lukas A, Pfaller W, Mueller SO, Bois FY, Dekant W, Jennings P. (2013) Application of integrated transcriptomic, proteomic and metabolomic profiling for the delineation of mechanisms of drug induced cell stress. J Proteomics. 2013 Feb 21;79:180-94. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23238060/
Limonciel A, Wilmes A, Aschauer L, Radford R, Bloch KM, McMorrow T, Pfaller W, van Delft JH, Slattery C, Ryan MP, Lock EA, Jennings P. (2012) Oxidative stress induced by potassium bromate exposure results in altered tight junction protein expression in renal proximal tubule cells. Arch Toxicol. 2012 Nov;86(11):1741-51. doi: 10.1007/s00204-012-0897-0. Epub 2012 Jul 4. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22760423/
Jennings P, Weiland C, Limonciel A, Bloch KM, Radford R, Aschauer L, McMorrow T, Wilmes A, Pfaller W, Ahr HJ, Slattery C, Lock EA, Ryan MP, Ellinger-Ziegelbauer H. (2012) Transcriptomic alterations induced by Ochratoxin A in rat and human renal proximal tubular in vitro models and comparison to a rat in vivo model. Arch Toxicol. 2012 Apr;86(4):571-89. doi: 10.1007/s00204-011-0780-4. Epub 2011 Nov 29. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22124623/
Sarkozi R. et al. (2011) Oncostatin M is a novel inhibitor of TGF-β1-induced matricellular protein expression. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2011 Nov, 301(5):F1014-F1025. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21816755/
Limonciel A, Aschauer L, Wilmes A, Prajczer S, Leonard MO, Pfaller W, Jennings P. (2011) Lactate is an ideal noninvasive marker for evaluating temporal alterations in cell stress and toxicity in repeat dose testing regimes. Toxicol In Vitro. 2011 Dec;25(8):1855-62. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2011.05.018. Epub 2011 May 24. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21635945/
Ellis JK, Athersuch TJ, Cavill R, Radford R, Slattery C, Jennings P, McMorrow T, Ryan MP, Ebbels TM, Keun HC. (2011) Metabolic response to low-level toxicant exposure in a novel renal tubule epithelial cell system. Mol Biosyst. 2011 Jan;7(1):247-57. doi: 10.1039/c0mb00146e. Epub 2010 Nov 19. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21103459/
Wieser M, Stadler G, Jennings P, Streubel B, Pfaller W, Ambros P, Riedl C, Katinger H, Grillari J, Grillari-Voglauer R. (2008) hTERT alone immortalizes epithelial cells of renal proximal tubules without changing their functional characteristics. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2008 Nov;295(5):F1365-75. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.90405.2008. Epub 2008 Aug 20. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18715936/
Licence Conditions
The business concept of Evercyte is to out-license telomerized cells to our customers. The license conditions depend on whether the contract partner is a for profit or a nonprofit organization and the intended use of the cells.
Nonprofit organizations
On time payment for unlimited use: EUR 1700
Profit organizations
Pharmaceutical – chemical – cosmetic industries
Contract research organizations (CRO)
Initial license fee for 3 months: EUR 2700Annual license fee R&D: royalty based
Customer Reviews
“I have had the pleasure of working with Evercyte for the last few years. We continually rely on Evercyte because of the high-quality data that they produce, their diligent responsiveness, and their excellent customer service.”
Josh Garlich, Senior Research Scientist, Apellis Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
“Cytonus has been working with Evercyte from many years as they are a trusted partner and have always delivered the highest quality cell lines to advance our platform. We routinely draw on their expertise to meet cellular engineering challenges and they have not disappointed.”
Remo Moomiaie-Qajar, Cytonus Therapeutics, Inc.